When most people consider heart health optimization, they default to conventional lipid management and saturated fat restriction protocols.
This approach, while foundational, overlooks a critical regulatory system that influences cardiovascular disease risk.
The emerging research reveals a more sophisticated relationship: your gut microbiome functions as a metabolic control center that actively regulates cholesterol synthesis, inflammatory responses, and arterial health.
I initially approached this connection through personal observation.
Each time I prioritized gut microbiome optimization—through strategic fiber increases, plant protein integration, and processed food elimination—my cholesterol markers improved substantially.
My energy stabilized. My digestive function became notably more efficient.
This pattern warranted deeper consideration.
What I discovered fundamentally upgraded my understanding of cardiovascular disease prevention: your gut microbiome doesn't merely assist with digestion. It operates as a regulatory system for inflammation management, lipid metabolism, and the production of compounds that directly influence cholesterol levels.
When your microbiome maintains optimal bacterial populations, it:
→ Reduces LDL cholesterol that contributes to arterial plaque formation
→ Supports HDL cholesterol that provides cardiovascular protection
→ Modulates systemic inflammation linked to heart disease and metabolic dysfunction
→ Regulates glucose and lipid metabolism, reducing insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome risk
When bacterial populations become imbalanced, the systemic effects cascade throughout your cardiovascular system—elevating LDLC, increasing inflammatory markers, and potentially accelerating your risk for hypertension, atherosclerosis, and cardiac dysfunction.
The encouraging reality: our microbiome composition is modifiable.
Through dietary modifications, we can cultivate bacterial populations that actively support optimal cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and provide long-term cardiovascular protection—without restrictive protocols or pharmaceutical intervention.
How Our Gut Functions as a Longevity Control System Beyond Digestion
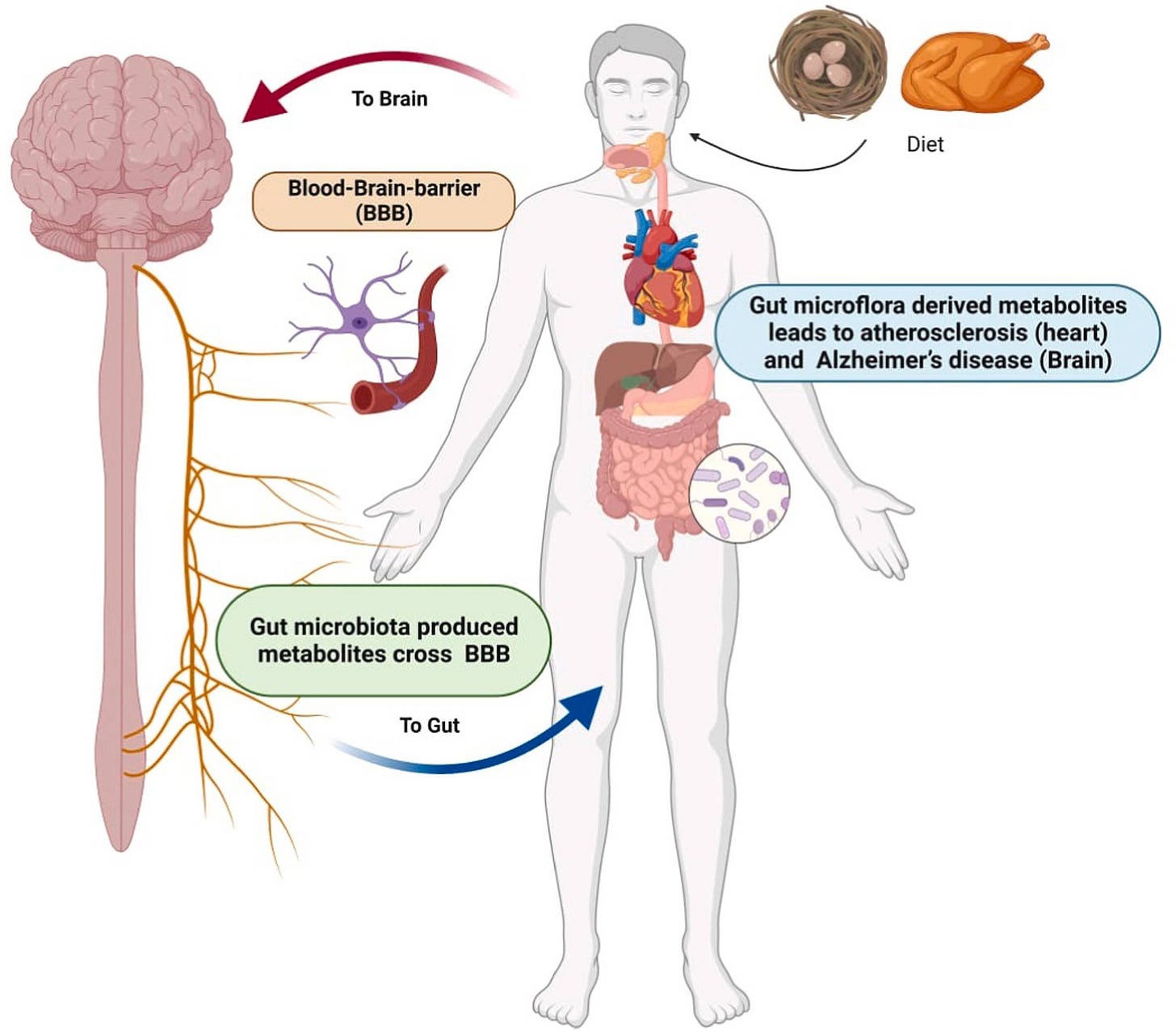
Our gut microbiome operates as what researchers now recognize as a "second brain"—a complex ecosystem that regulates immune function, synthesizes essential nutrients including vitamin K, and directly influences cardiovascular health through multiple biological pathways.
When this bacterial ecosystem becomes disrupted—a condition termed dysbiosis—the long-term health consequences extend far beyond digestive symptoms:
Hypertension (elevated blood pressure)
Coronary artery disease
Heart failure
Atherosclerosis
Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome
For my own optimization, prioritizing gut-supportive food selections has proven to be among the most effective longevity interventions I've implemented.
My inflammatory indicators decreased measurably and my energy patterns became significantly more stable—all achieved through dietary modification rather than restrictive elimination protocols.
However, dramatic overhaul isn't necessary for meaningful results.
Even graduated modifications—strategic fiber increases, cleaner fat sources, and increased plant-protein integration—can transform our guts into an active partner in longevity optimization rather than a source of inflammatory burden.
In this comprehensive analysis, I'll examine:
The specific biological mechanisms linking gut health to cardiovascular disease prevention
Why eliminating certain foods can measurably improve your longevity markers
The implementation protocol I developed for sustainable gut-heart optimization
The Gut-Cardiovascular Axis: Understanding the Biological Mechanisms
Our gut microbiome—comprising trillions of microorganisms—operates far beyond simple food breakdown. Among its numerous regulatory functions, it directly influences:
Systemic inflammation modulation, which affects cholesterol metabolism and cardiac function
Gut barrier integrity maintenance, preventing harmful compounds from entering systemic circulation
Essential vitamin synthesis, including vitamin K, which supports vascular health and calcium regulation
When this microbial ecosystem becomes compromised—characterized by harmful bacterial overgrowth and beneficial species depletion—it triggers chronic inflammatory cascades and disrupts lipid metabolism in ways that burden cardiovascular function.
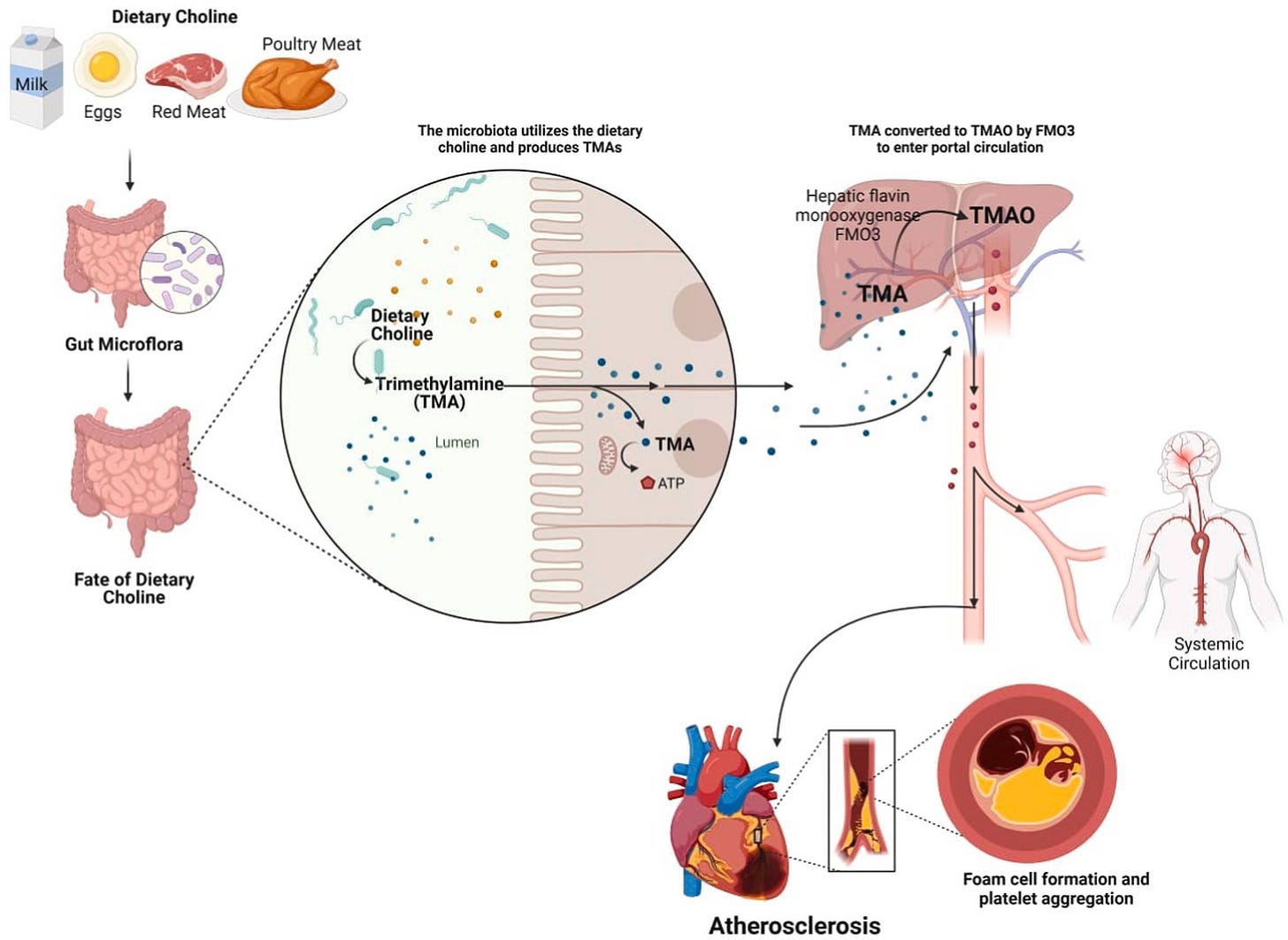
One compound that has gained research attention is trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO).
Specific pathogenic bacteria convert nutrients found in red meat, eggs, and seafood into TMAO—a metabolite strongly associated with arterial plaque acceleration, myocardial infarction, and stroke risk.
The biological pathway operates as follows: when we consume animal proteins high in choline, carnitine, and phosphatidylcholine, certain gut bacteria produce trimethylamine (TMA). Our liver then oxidizes TMA into TMAO, which directly promotes atherosclerosis through multiple mechanisms including enhanced platelet aggregation and arterial wall inflammation.
How does microbiome dysbiosis compromise cardiovascular performance and longevity optimization?
The evidence reveals several critical pathways.
Atherosclerosis
Mechanism: Fatty plaques accumulate in arteries, progressively restricting blood flow
Gut involvement: TMAO production accelerates plaque formation and arterial inflammation
Longevity impact: Reduced circulation compromises tissue oxygenation, repair capacity, and cognitive function
Hypertension
Mechanism: Chronic elevated blood pressure that creates sustained cardiovascular strain
Gut involvement: Dysbiosis reduces beneficial short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production that naturally regulates blood pressure
Longevity impact: Persistent vascular stress accelerates biological aging and increases stroke risk
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Mechanism: Progressive narrowing or blockage of arteries supplying cardiac muscle
Gut involvement: Elevated TMAO levels promote cholesterol accumulation and arterial wall damage
Longevity impact: Compromises cardiac efficiency and stress resilience; CAD remains a leading mortality factor
Heart Failure
Mechanism: Progressive decline in cardiac pumping efficiency
Gut involvement: Dysbiosis and elevated TMAO levels worsen systemic inflammation and accelerate cardiac muscle deterioration
Longevity impact: Substantially reduces exercise capacity, energy levels, and overall quality of life
Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Mechanism: Irregular cardiac rhythm that increases stroke and heart failure risk
Gut involvement: Dysbiosis increases systemic inflammation and disrupts cardiac electrical signaling
Longevity Impact: Emerging research identifies gut bacterial imbalances as significant AF risk factors
Dyslipidemia (Cholesterol Dysregulation)
Mechanism: Abnormally elevated cholesterol or triglyceride levels in circulation
Gut involvement: Dysbiosis disrupts bile acid metabolism, which is essential for cholesterol regulation and elimination
Longevity impact: Increases cardiovascular and metabolic dysfunction risk with aging
For my own optimization protocol, shifting toward gut-supportive foods produced measurable improvements: my digestive function stabilized, and energy patterns became significantly more predictable.
This was achieved through strategic modification.
Up next, I’ll show you exactly what that looks like in practice.
My Approach to Cardiovascular and Cognitive Optimization Through Gut Architecture
1. How Strategic Protein Selection Reduces Cardiovascular Risk While Supporting Cognitive Function
I didn't set out to eliminate all animal proteins—but after tracking my cholesterol levels creeping toward the high end of normal, I designed a deliberate intervention.
I temporarily paused meat (red or white), eggs, dairy and seafood. I wanted to measure how this shift would impact my inflammation markers, digestive function, and complete lipid profile. This was a controlled self-experiment, not a philosophical position.
I was also increasingly concerned about the documented toxin accumulation in seafood and the undisclosed chemical additives used in conventional food processing—many of which bypass standard labeling requirements.
What I discovered surprised me.
Below, you'll see my actual labs after just 6 weeks—
And the approach I developed to get there.
Here is the Vault 5×5 Fiber Matrix Framework™ that helps you support your gut-brain-lipid axis—so you can lower:
cardiovascular risk,
colon cancer risk
inflammation and cognitive decline risk linked to low microbial diversity
—all without psyllium husk, fiber supplements, or counting grams—
and while actually enjoying your food.
If you’d like to access The 5-Phase Gut-LDL-C Blueprint for Lower Cholesterol + Reduced Cardiovascular Risk as a one-time option (without an ongoing subscription), you can do so here:
Alternatively, Vault Insider Exclusives receive this complete system as part of their membership, along with all previous & future optimization frameworks + workbooks throughout the year.